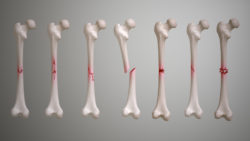
Osteomyelitis is a condition in which there is an infection in the bone. It is a rare condition, but one that can be quite serious. It is a bacterial infection. The infection may reach the bone through the bloodstream or may originate in the bone itself in case of exposure of injured bones to germs.

Osteomyelitis could be acute or chronic. In case of acute osteomyelitis, the condition develops rapidly and is accompanied by intense pain. Chronic osteomyelitis is slow in developing and the symptoms are subtle.
Causes
The most common cause of Osteomyelitis is Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. These are bacteria that are found on the skin. These germs enter the body through various ways highlighted below:
- Through the bloodstream:
A person may have an infectious disease elsewhere in the body and the bacteria may travel through the bloodstream and spread to the bone, causing inflammation and infection in the bone.
- Injury:
Injuries such as open fractures can cause the germs to enter the body and infect the bone.
- Surgery:
Surgery around a bone may also expose the bone to bacteria and lead to osteomyelitis.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of osteomyelitis are pain, fatigue, swelling, redness, warmth, fever and drainage of pus. However, in some cases where the condition is acute additional symptoms such as, chills, excess sweating, lower back pain in case the infection is in the spine, swelling in ankles and feet and decrease of motion in a joint.
Risk factors
Osteomyelitis affects both children and adults.
In
adults, it occurs mostly in the vertebrae and the pelvic region.
In
children it usually occurs in the long bones such as those in the arms and legs.
People who are more likely to develop Osteomyelitis are those who have a weakened immune system due to medical conditions such as diabetes, sickle cell disease, recent injury, poor blood supply, bone surgery and long term use of steroids.
Treatment
Treatment of osteomyelitis is usually approached with the purpose of eliminating the infection and to prevent it from developing into a chronic condition. Chronic osteomyelitis can lead to deformity and fractures and it is quite important to treat it as early as possible. Prescribing antibiotics and pain medication is commonly the foremost step in the treatment of this condition. Antibiotics may be administered through IV for a few weeks and then given through oral pills. However, more serious or chronic condition may require surgery in which the infected tissues and bone may have to be removed in some cases.
The earlier Osteomyelitis is treated, the better the chances are for a complete recovery usually. Apart from the inconvenience of pain, other symptoms, continuous treatment, bringing osteomyelitis under control quickly increases the probability of complete recovery. It is very important to clean wounds and cuts immediately.
Disclaimer: The information in no way constitutes, or should be construed as medical advice. Nor is the above article an endorsement of any research findings discussed in the article an endorsement for any of the source publications.
Sources-
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/178819.php
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9495-osteomyelitis/management-and-treatment
- https://www.medicinenet.com/osteomyelitis/article.htm
- https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/osteomyeltis-treatment-diagnosis-symptoms#2
Any injury to the bone resulting in damage is a fracture. Most fractures occur due to the high impact of force, such as falls or accidents, but some may happen without too much strain on the bones because the bones are weak due to certain medical conditions such as osteoporosis or some cancers.
Read More..
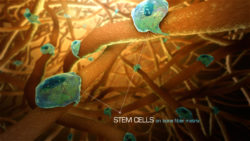
Perhaps the smartest cells in the human body are the stem cells. As long as they are placed in the right conditions and right signals are sent to them, they can possibly replicate any part of the body. However, knowing the right conditions and the right signals for synthesizing the desired tissue is easier said than done.
Read More..